- English
- 日本語
- 한국어
- Deutsch
- Français
- Español
No data
官方服务号
招聘公众号
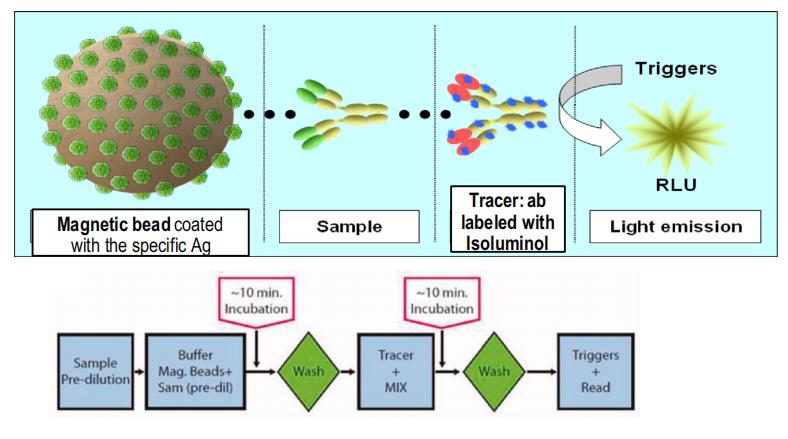
Magnetic Particle (MP) Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) is an analytical method that combines the flexibility of magnetic beads with the sensitivity and specificity of CLIA. Instead of immobilizing proteins or antibodies within the well plate, magnetic beads provide a significant increase to the sample contact surface area, capture efficiency, and automation capabilities. As such, MPCLIA is becoming frequently adopted in disease diagnostics, chemical reaction monitoring, and many other research fields.
Besides the use of magnetic beads as the base scaffold, the biggest deviation of MPCLIA from traditional ELISA is the detection through chemiluminescence. By utilizing a chemical reaction to excite substances like horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and acridinium ester(AE), photons are released that can be measured using a specialized chemiluminescence reader. In comparison, CLIA methods have often shown higher sensitivity, specificity, and linear ranges over traditional ELISA.
Chemiluminescence Detection Mechanism
Colorimetric (ELISA) Detection Mechanism
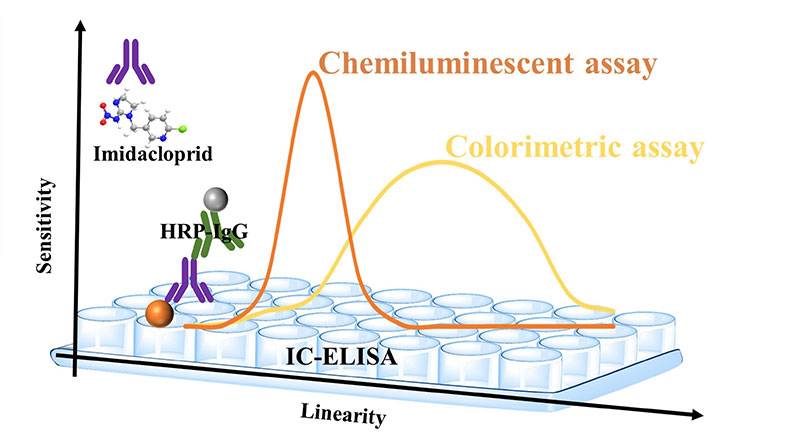
Magnetic Particle (MP) Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) is an analytical method that combines the flexibility of magnetic beads with the sensitivity and specificity of CLIA. Instead of immobilizing proteins or antibodies within the well plate, magnetic beads provide a significant increase to the sample contact surface area, capture efficiency, and automation capabilities. As such, MPCLIA is becoming frequently adopted in disease diagnostics, chemical reaction monitoring, and many other research fields.
Besides the use of magnetic beads as the base scaffold, the biggest deviation of MPCLIA from traditional ELISA is the detection through chemiluminescence. By utilizing a chemical reaction to excite substances like horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and acridinium ester(AE), photons are released that can be measured using a specialized chemiluminescence reader. In comparison, CLIA methods have often shown higher sensitivity, specificity, and linear ranges over traditional ELISA.
Chemiluminescence Detection Mechanism

Colorimetric (ELISA) Detection Mechanism

Magnetic Particle (MP) Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) is an analytical method that combines the flexibility of magnetic beads with the sensitivity and specificity of CLIA. Instead of immobilizing proteins or antibodies within the well plate, magnetic beads provide a significant increase to the sample contact surface area, capture efficiency, and automation capabilities. As such, MPCLIA is becoming frequently adopted in disease diagnostics, chemical reaction monitoring, and many other research fields.
Besides the use of magnetic beads as the base scaffold, the biggest deviation of MPCLIA from traditional ELISA is the detection through chemiluminescence. By utilizing a chemical reaction to excite substances like horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and acridinium ester(AE), photons are released that can be measured using a specialized chemiluminescence reader. In comparison, CLIA methods have often shown higher sensitivity, specificity, and linear ranges over traditional ELISA.
Chemiluminescence Detection Mechanism

Colorimetric (ELISA) Detection Mechanism

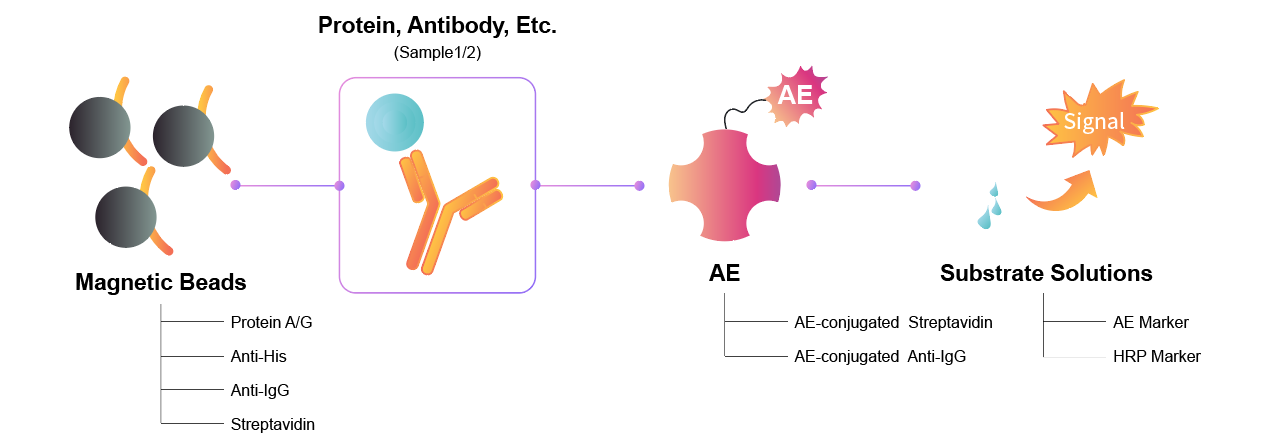
Magnetic Particle (MP) Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) is an analytical method that combines the flexibility of magnetic beads with the sensitivity and specificity of CLIA. Instead of immobilizing proteins or antibodies within the well plate, magnetic beads provide a significant increase to the sample contact surface area, capture efficiency, and automation capabilities. As such, MPCLIA is becoming frequently adopted in disease diagnostics, chemical reaction monitoring, and many other research fields.
Besides the use of magnetic beads as the base scaffold, the biggest deviation of MPCLIA from traditional ELISA is the detection through chemiluminescence. By utilizing a chemical reaction to excite substances like horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and acridinium ester(AE), photons are released that can be measured using a specialized chemiluminescence reader. In comparison, CLIA methods have often shown higher sensitivity, specificity, and linear ranges over traditional ELISA.
Chemiluminescence Detection Mechanism

Colorimetric (ELISA) Detection Mechanism

Magnetic Particle (MP) Chemiluminescent Immunoassay (CLIA) is an analytical method that combines the flexibility of magnetic beads with the sensitivity and specificity of CLIA. Instead of immobilizing proteins or antibodies within the well plate, magnetic beads provide a significant increase to the sample contact surface area, capture efficiency, and automation capabilities. As such, MPCLIA is becoming frequently adopted in disease diagnostics, chemical reaction monitoring, and many other research fields.
Besides the use of magnetic beads as the base scaffold, the biggest deviation of MPCLIA from traditional ELISA is the detection through chemiluminescence. By utilizing a chemical reaction to excite substances like horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and acridinium ester(AE), photons are released that can be measured using a specialized chemiluminescence reader. In comparison, CLIA methods have often shown higher sensitivity, specificity, and linear ranges over traditional ELISA.
Chemiluminescence Detection Mechanism

Colorimetric (ELISA) Detection Mechanism

| Product type | Cat. No. | Product Description | Preorder/Order |
|---|
| Product type | Cat. No. | Product Description | Preorder/Order |
|---|

| Product type | Cat. No. | Product Description | Preorder/Order |
|---|

| Product type | Cat. No. | Product Description | Preorder/Order |
|---|
